|
|
|
The management of thromboembolic disease in
HIV-infected patients is much the same as for anyone else.
- Manage the acute thrombotic episode.
- Evaluation for underlying causes.
- Long term follow-up and management.
- Heparin and warfarin.
- Lookout for possible interactions with
antiviral agents.
- Prompt treatment of intercurrent
infections has been shown to reduce thrombotic events.
|
 |
- In treatment of PE, subcutaneous
low-molecular weight heparin has been reported to be as effective and
safe as IV infractionated heparin.
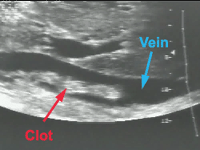
- The picture at the right is of an
ultrasound showing a deep leg vein thrombosis.
- Note its only attached at one end and
about to break free.
|
 |
A 34 year-old man is brought
in unconscious. |

